Theme: Global Health a major topic of concern in Epidemiology Research and Public Health study
Epidemiology Meet 2019
- About Conference
- Scientific Session / Tracks / Key Topics Epidemiology and Public Health Conference 2019
- Market Analysis for Epidemiology Meet 2019
- Epidemiology Conference 2019: News & Recent Updates
EPIDEMIOLOGY MEET 2019
The 7th Epidemiology and Public Health Conference, will be held at Dubai, UAE during June 17-18, 2019
The theme falls on “Global Health a major topic of concern in Epidemiology Research and Public Health study”.
Epidemiology Meet 2019 in conjunction with its institutional partners and Editorial Board Members are delighted to invite you all to the 7th Epidemiology and Public Health Conference, to share experiences and best practices through invited keynote, symposia, workshops, plenary lectures, invited sessions and posters covering a range of topics and important issues which affect us all from the research to the practical implementations.
Epidemiology Meet 2019 will converge on the rising health issues and unexplored fields of diseases and invigorate developments connected to every aspect of public health, epidemiology, nutrition and Physicians research which provides new opportunities for specialists of all over the world to congregate exchange, organize and discover new technologies and research ideas.
We unreservedly welcome all the prominent researchers, students, professors, doctors, nutritionists public health professionals, nutritionists, epidemiologists, pathologists, statisticians, clinicians, business professionals, foundation leaders, Presidents, CEO, directors, direct service providers, researchers, academicians, advocates, policymakers and delegates to participate in upcoming public health conference to witness valuable scientific talks and discussions and to be a part of our conference by participating in 7th Epidemiology and Public Health Conference and to contribute to the innovative future ideas about Public health, Epidemiology and nutrition.
Target Audience
- Doctors
- Professors
- Physicians
- Researchers
- Social workers
- Business Analysts
- Nurse practitioners
- Foundation Leaders
- Associate professors
- Healthcare Investors
- Health care industries
- Health care universities
- Health care professionals
- Medical Lab Technicians
- Health care administrators
- Family medicine specialists
- Public Health Professionals
- Primary health care specialists
- Health care associations and societies
Benefits of Attending:
- Exchange ideas and meet people like leading epidemiologists, pathologists, veterinarians, microbiologists, clinicians, public health professionals and researchers from more than 40+ countries
- Examine quality initiatives that can be applied in the practice
- Talk about ways to collaborate in putting quality initiatives in place all through the epidemiology study and epidemiology and prevention of vaccine-preventable diseases
- Members can gain complete access to a core audience of experts and decision-makers and can augment perceivability through branding and networking at the conference
- Discussing key news and challenges with superior level speakers.
The open exchange of ideas and the freedom of thought and expression are the major motto of our conference. Epidemiology Meet 2019 will focus on various topics like Epidemiology and Public Health, Health and Nutrition, Oral & Dental Health, Cancer Epidemiology, Nursing and Health Care, Veterinary Public Health, Child and Adolescent Health, Health Systems and Economics, Chronic and Infectious Diseases, Healthcare & Hospital Management, Mental Health and Mental Disorders, Cardiac Disorders & its complications, Metabolism and Metabolic Disorders, Public Health Policy and Administration, Environment, Climate and Urban Health, Biomedical and Health Care Technologies, Reproductive Medicine & Women’s Health etc.
Epidemiology Meet 2019 has choose Dubai, as today date there are a number of world-leading companies, research institutes and individuals which are active in various fields.
We will be glad to be acquainted with you at Dubai, to enjoy the top-notch conference services and accommodation, visit the World heritage sites and enjoy the enchanting cuisine and delightful shopping.
With presentations, workshops panel discussions, and roundtable discussions, we involve every topic from top to bottom, from global comprehensive issues to strategies to tactical issues
We hope to have your presence at Epidemiology Meet 2019!
Track 1: Epidemiology and Public Health
The word epidemiology comes from the Greek word Epi, connotation "on or upon," demos, meaning "people," and logos, meaning "the study of”. Epidemiology is a quantitative regulation built on a functioning knowledge of likelihood, statistics, and sound investigation methods; a method of causal interpretation based on developing and testing theories relating to incidence and deterrence of morbidity and mortality; and an implement for public health conflict to encourage and safeguard the public's health.
-
Epidemiology and Aging
-
Epidemiology and Obesity
-
Epidemiology and Nutrition
-
Epidemiology and Outbreak
-
Epidemiology and Disability
-
Epidemiology and Risk factor
-
Epidemiology and Surveillance
-
Epidemiology and demography
-
Epidemiology and People Health
-
Epidemiology and Mental Health
-
Epidemiology and Childhood obesity
-
Epidemiology and Community Health
-
Epidemiology and Evidence based practice
Track 2: Health and Nutrition
A balanced diet is fundamental for good health and food gives energy, protein, vital fats, vitamins and minerals for a body to survive, grow and work properly. Diet and nutrition which take part in a significant role in major causes of fatality, poor health and inabilities like coronary heart disease, stroke, hypertension, atherosclerosis, obesity, cancer, osteoporosis, dental caries, and gallbladder disease. It clarifies the relations of nutrients and other food substances with the connection to the maintenance of a living being, growth and health diseases.
Present nutritional guiding principle advocates reducing free sugars, particularly fructose from sugared beverages, but it is uncertain whether this holds for all food sources of these sugars.
-
Corelation Studies
-
Nutrition Deficiencey Syndromes Epidemiology
-
Limitations In Nutrition Epidemiology Research
-
Epidemiological Approach To Diet And Diseases
-
Malnutrition And Occurance Of Diseases Epidemiology
Track 3: Oral & Dental Health
Research conducted in the field of oral health epidemiology present data on distinctive biological forms and on infections of the oral cavity, distinguish populations at a chance of oral disease are in need of special care, and compare regional, ecological, social, and get to similitudes and contrasts in dental care between populaces. Oral issues, including terrible breath, dry mouth, canker or cold bruises, TMD, tooth rot, esophagus or oral cancer, or thrush are all treatable by means of appropriate analysis and care. Proper oral and dental cleanliness can offer help get rid of awful breath, tooth rot, and gum illness and can proffer aid to any person to preserve teeth as we get older.
-
Epidemiology and Drug
-
Epidemiology and Aging
-
Epidemiology and Alcohol
-
Epidemiology and Hygiene
-
Epidemiology and Smoking
-
Epidemiology and Gentle Health
-
Epidemiology and Quality of Life
-
Epidemiology and preventive dentist
-
Epidemiology and learning disabilities
Track 4: Cancer Epidemiology
Oncology epidemiology is a branch of epidemiology which deals with the preclusion, diagnosis & treatment of cancer. Numerous risk factors for cancer are liquor consumption, tobacco, smoking, growing older etc. The world suffers a serious problem related to cancer. Fatality due to cancer is often more than a past year. Various technics & drugs are presented in the market for a cancer cure.
Eight million people pass away because of cancer around the globe every year. Men are considerably more probable than women to be diagnosed with cancer in their life span, and for the majority of cancers, the chance of developing the malady rises drastically with time. Aging immune system may explain age-related cancer risk increase.
-
Epidemiology and Lung Cancer
-
Epidemiology and Breast Cancer
-
Epidemiology Colorectal Cancer
-
Epidemiology and Cancer Research
-
Epidemiology and Clinical Research
-
Epidemiology and Cancer Prevention
Track 5: Nursing and Health Care
Public health nursing is a branch of nursing along with the specialty in Public health. Public health nurses are a community of nurses who are implicated in coordination between community and one who knows well concerning to clinical methods and treatment of wellbeing. Public health nursing is one of the abandoned fields of the health sector.
-
Community Health Nursing
-
Occupational Health Nursing
-
Nursing management and education
-
Nuclear Education in Public Health and Nursing
Track 6: Veterinary Public Health
Veterinary epidemiology is a vital component in a numeral universal extensive challenge relating to disease control, food safety measures and climate change. Subsequently, there are a necessitate improvements in our ability to recognize, predict and respond to patterns and elements of disease and to manage outbreaks.
-
Zoonosis
-
Animal products
-
Borne infections
-
Veterinary Pathology
-
Veterinary parasitology
-
Communicable diseases
-
Veterinary parasite diseases
-
Veterinary clinical pathology
-
Injuries from exposure to animals
-
Chemicals and drugs used for animals
-
Exposure to hazards arising from animals
Track 7: Child and Adolescent Health
An adolescent is the youths in the populace. Adolescents experience the need for health services which pretence various challenges intended for the healthcare system than in children and adults, because of the fast-evolving physical, intellectual and emotional development. Youth’s health deals with the safety, deterrence, detection, and treatment of the adolescent age group and well-being. The terms adolescent and adolescence health are interchangeably used.
-
Chronic illness
-
Youth health nursing
-
Adolescent medicine
-
Diseases in adulthood
-
Drug and Alcohol services
-
Physical and Sexual Assault
-
Health and social challenges
-
Nutrition and physical activity
Track 8: Health Systems and Economics
Health economics is linked with the value, behavior, efficiency & efficacy in the production and consumption of healthcare care & health-affecting behaviors such as consumption of alcohol, smoking etc. Health care policies incorporate the plans, actions & decisions that are taken to achieve exact healthcare objectives within an association. It includes National Health policy, personal health care policy, Nursing Healthcare policy, pharmaceutical policy, and public health policy such as vaccination policy, tobacco control policy and breastfeeding promotion policy.
-
Health Economics
-
Evidence based Public Health
-
Public Health Laws and Regulations
-
Quality Assurance and Improvement
-
Public Health Policy, Leadership and Financing
-
Health Insurance: Implications for Public Health
-
Global Evidence on Women’s Health and The Role of Social and Economic Factors
-
Public Health Workforce Capacity Building (Training, Mentoring, Infrastructure Improvement)
-
Health Systems Strengthening Through Human Resource Capacity Building, Effective Health Management and Efficient Financing.
Track 9: Chronic and Infectious Diseases
The epidemiology of infectious disease includes contemplating the predominance, recurrence, and determinants of contaminations in the populace. Irresistible diseases live one of the most unfavourable causes of dreariness and death around the world. Human immunodeficiency virus, papillomavirus, other genital tract contaminations affecting women, and other sexually transmitted diseases.
-
Epidemiology and HIV
-
Epidemiology and Etiology
-
Epidemiology and Infection
-
Epidemiology and Diseases
-
Epidemiology and Zoonosis
-
Nutritional Health And Researches
-
Epidemiology and Disease control
-
Epidemiology and intrinsically resistant
-
Epidemiology and Incidence chronic disease
-
Epidemiology and prevalence chronic disease
Track 10: Healthcare & Hospital Management
Health care systems are the systems or organizations which bring health care services to accomplish for the wellbeing of the society. There is a diverse range of healthcare systems surrounding the world with many organizational structures and institutions which deliver healthcare. The nation must come to a decision and plan the healthcare systems lying on their need and resources.
-
Healthcare quality
-
Health informatics
-
Health care systems
-
Healthcare transport
-
Disease management
-
Health administration
-
Managerial epidemiology
-
Medical case management
-
Health care efficiency measures
Track 11: Mental Health and Mental Disorders
Psychological disorders are health conditions that are characterized by changes in the state of mind, mood and behaviour that are related to pain or potentially debilitated working. Mental illness is the term that alludes by on the whole to all diagnosable mental disorders. Mental disorders add to a large group of issues that may add in disability, death. Most well-known reasons for inability are mental disorders. The consequent diseases burden of mental illness is among the supreme of all diseases. In an investigation, an expected 18.1% (43.6 million) of U.S. adults ages 18 years or more endured from the mental disorder and 4.2% (9.8 million) of European suffered from a seriously devastating mental ailment. Neuropsychiatric disorders are the main basis of disability in the Asian countries, demonstrating 18.7% of all years of life lost to incapability and premature death. Moreover, suicide is the tenth driving reason for death around the world, representing the deaths of around 43,000 in 2014.
-
Anxiety
-
Schizophrenia
-
Bipolar disorder
-
Personality disorders
-
Sexual and gender disorders
-
Obsessive-compulsive disorder
Track 12: Cardiac Disorders & its complications
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) includes a class of Heart diseases or blood vessels. Cardiovascular disorder involves coronary artery diseases such as angina and myocardial infarction or heart attack. Other CVDs comprise stroke, coronary artery bypass grafting, endocarditis, rheumatic heart disease, heart failure, venous thrombosis, atherosclerosis, heart transplantation, heart valve surgery, Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), Clot-busting medicine, Cardio-oncology, Open heart surgery, Cardiomyopathies, Adult congenital heart disease etc.
-
Prevention of CVD
-
Cardiovascular disease (CVD)
-
Cardiovascular Health and Diseases Health
-
Multidisciplinary workforce in cardiovascular epidemiology
-
Recognition of the social determinants of cardiovascular health and disease
-
Recognition of the essential role of community-based approaches to cardiovascular health
Track 13: Metabolism and Metabolic Disorders
Endocrinology is a branch of medicine managing with the endocrine system, metabolism & its disorders and its particular secretions known as hormones, growth support, and malignant cells, which possibly will lead to Polycystic ovary syndrome, Diabetes mellitus, Growth hormone deficiency and growth disorders, Follicular and Medullary thyroid cancer, Hyperlipidemia, Osteoporosis, Lipid Control in Diabetes and Metabolic Syndrome, Thyroid growths, under activity/over activity.
-
Hormones
-
Osteoporosis
-
Hyperlipidemia
-
Diabetes mellitus
-
Endocrine system
-
Growth disorders
-
Thyroid growths
-
Metabolic Syndrome
-
Lipid Control in Diabetes
-
Metabolism & its disorders
-
Polycystic ovary syndrome
-
Growth hormone deficiency
-
Growth promotion and malignancy
Track 14: Public Health Policy and Administration
Health Economics results are to analyze the burden and etiology of infectious maladies and non-communicable diseases in the populace and to arrange and distribute data that will assist improve the quality of health safety across nations. Health Economics policies address the important issues over the global health and encourage relations and collaboration across the people.
-
Epidemiology and Ethics
-
Epidemiology and Anthropology
-
Epidemiology and Medical Sociology
-
Epidemiology and Medical Anthropology
Track 15: Environment, Climate and Urban Health
The earth was the unbiased system before, after the human evolution and civilization the ensemble of the mother nature has been troubled by human toxic products and waste from the industrialization. So Universal environmental health is significant to survive and lead a healthy life. International environmental health deals with the study of health care, prevention and effective method to be taken to save the health of the environment.
-
Environmental factor
-
Environmental health
-
Environmental diseases
-
Environmental hazards & human health
Track 16: Biomedical and Health Care Technologies
Healthcare and technology can be named as the health information technology or Health IT. The health information technology is the broad concept which gives knowledge concerning a group of technologies to share, store and analyse the health information. In recent days, most of the healthcare units and suppliers are using health IT to enhance patient health care. Health IT also gives services in building up communication with doctor and patient precisely, learn and share information about their health and actions to be taken to increase the health quality of the patient.
-
e-Health
-
Health informatics
-
Clinical decision support (CDS)
-
Electronic medical records (EMR)
-
Electronic health records (EHRs)
-
Health information technology ( HIT)
-
Computerized physician order entry (CPOE)
-
Electronic medication administration records (eMAR)
-
Bar-coding at medication administration (BarA or BCMA)
Track 17: Reproductive Medicine & Women’s Health
Reproductive medicine is the branch of medical science which deals with the determination, prevention, and management of issues in reproduction. Its aims include maintaining and improving the reproductive health and allowing people to have children at the time of their comfort. Reproductive medicine plays a significant role in women’s wellbeing where the mother’s health openly influences the health quality of children.
-
Reproductive Cloning
-
Health in Pregnancy
-
Maternal and Child Health
-
Reproductive Endocrinology
-
Autoimmune Diseases in Women
-
Perinatal and Reproductive Health
-
Placentation and placental function
-
Biomarkers in Reproductive Medicine
-
Regenerative Medicine and their Application
Track 18: Case Report on Epidemiology and Public Health Research
Most important areas of epidemiological study include disease causation, forensic epidemiology, occupational epidemiology, screening, biomonitoring, transmission, outbreak investigation, disease surveillance, and comparisons of treatment effects such as in clinical trials.
Epidemiologists depend on other systematic disciplines like biology to change for the better comprehend disease processes, statistics to make efficient use of the data and draw suitable conclusions, community sciences to better known proximate and distal causes, and engineering for exposure assessment.
-
Etiology
-
Community Health
-
Social Epidemiology
-
Clinical Epidemiology
-
Obesity & Public Health
-
Molecular Epidemiology
-
Diabetes & Public Health
-
Psychiatric Epidemiology
-
Homeopathy & Public Health
-
Occupational Health & Safety
-
Patient Safety & Quality Healthcare
-
Epidemiology and Genomic Research
-
General Practice & Primary Healthcare
-
Epidemiology and Antibiotic Resistance
Epidemiological reconnaissance is conducted all over to examine the etiological components of disease and causes for spreading and its preventative measures. This conference gives the international platform for recent research on the uprising and re-rising diseases, communicable diseases, Non-communicable diseases. This conference has the extent to be the source of the medical specialty variables like origin, spread and up to date status of different diseases and disorders causing deaths in several nations.
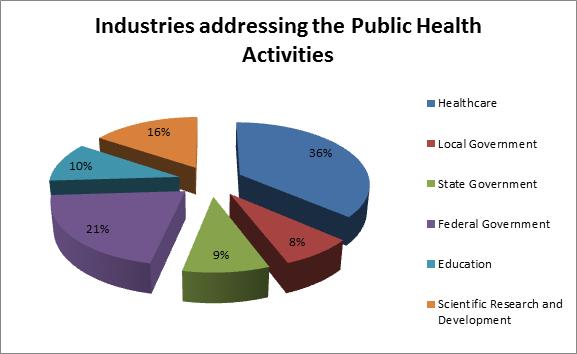
Public health and Epidemiology Research mainly centers on the health of the public in collective. It addresses observing and reconnaissance of nutrition grade and nutritional environments in communities or populaces at risk recognizes and investigates behavioral, sociocultural, monetary, political, and ecological determinants of nutrition-related community health. The fundamental goal of public health is the biologic, physical and psychological well-being of the general public by prolonging existence and advancing a healthy standard of living. It incorporates pre-planning of natural and man-made calamities. Numerous health systems around the world integrate public health activities and obligations in a different way, depending on the arrangement, financing, and accessibility of healthcare in population. The main purpose is catching up through decades of health economics and outcomes research (HEOR) experience broadcasting the significance of real-world insights in healthcare determination. HEOR is decisive in taking innovative treatments from the lab to the commercial center. Combining scientific techniques, deep therapy subject information and a practical understanding of the marketplace. Health economists measure multiple types of monetary information: expenses, charges, and expenditures as externalities evolve frequently while taking into consideration health and health care, especially in the context of infectious disease.
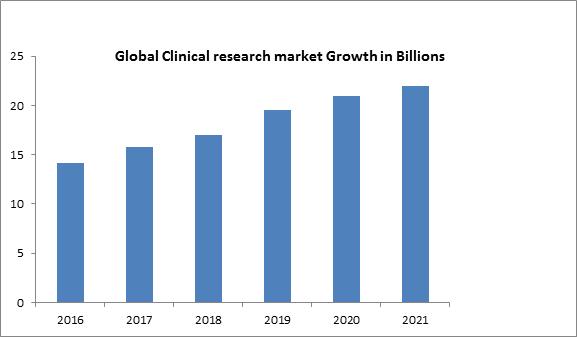
The worldwide Pharmacoepidemiology and clinical research market has been evaluated to reach USD 14.2 billion in 2016-2017 and is proposed to reach around USD 22 billion by the year 2021, rising at a CAGR (compounded annual growth rate) of 7.5%, throughout the estimated period 2016 to 2021. The clinical investigation includes the Clinical examination as an element of clinical research that follows a controlled convention. Clinical research is basically performed to assess the safety and efficiency of the newly developed sedate. Clinical test data is obligatory for additional endorsement of the drug and to bring it into the market.
Why to Attend???
Together with people from around the globe engrossed on discovery about Epidemiology and its signs of progress; this is your finest chance to accomplish the most important assembly of members from the Epidemiologist associates group. Headstart your most excellent chance to accomplish the most vital crowd of present and potential researchers, create a intersperse with new revelations in the study of disease spread and general Health and get name recognition at this 2-day occasion. Extensively celebrated speakers, the most recent ways, methodologies, enhancements, and the most up to date revives in Communicable Diseases Epidemiology, Cardiovascular Diseases therapeutic claim to fame, Cancer curative strength, generative, Perinatal and Pediatric Epidemiology.
Public Health Target Audience:
-
Health policy-makers
-
Health care administrators
-
Health care professionals
-
Ministry of Health staff at the policy, operational decision-making levels in central and decentralized units
-
Ministry of Planning staff working in the health sector
-
Health economists
-
Clinicians
-
Researchers who have the on-the-ground skills of health care delivery and want to understand the logic of health care as an industry
-
Graduates from health sciences and social sciences
-
IT professionals who are interested in structuring practical research that measures the impact of proposed programs and health policy changes
-
Students participating in the Master Health Sciences
-
Medical health officers - They will be able to provide better services to the consumer
-
Paramedical students – They manage various medical situations and economies of it and can be able to better advise the customers
-
Individual hospital facility are benefited as this facilitate them of the hospital and perceive what services are needed by the customers of the hospital and the way will they be funded.
-
Pharmaceutical and health insurance corporations will be benefited as this may facilitate in understanding the demand and provide varied health and insurance products and evaluate the economic viability of the same for the company.
Epidemiology Associations
- Italy National Institute of Health
- Royal Society for Public Health, UK
- Association of Chinese Epidemiology
- Thailand National Institute of Health
- Finnish Epidemiological Society (FES)
- Danish Epidemiological Society (DES)
- Spanish Society of Epidemiology (SSE)
- Egyptian Society of Epidemiology (ESE)
- Indian Public Health Association (IPHA)
- Japan Epidemiological Association (JEA)
- Saudi Epidemiological Association (SEA)
- Swedish Society of Epidemiology (SVEP)
- Romanian Society of Epidemiology (SRE)
- American College of Epidemiology (ACE)
- Italian Association of Epidemiology (AIE)
- Society for Epidemiologic Research (SER)
- Iranian Epidemiological Association (IrEA)
- Cameroon Society of Epidemiology (CaSE)
- German Society for Epidemiology (DGEpi)
- Netherlands Epidemiological Society (VvE)
- Association Medical Argentina (ADMISAL)
- Indian Society for Medical Statistics (ISMS)
- Epidemiological Society of Nigeria (EPiSON)
- American Public Health Association (APHA)
- Lebanese Epidemiological Association (LEA)
- Sociedad Española de Rheumatology, Spain
- Sweden The Public Health Agency of Sweden
- Portuguese Association of Epidemiology (APE)
- Australasian Epidemiological Association (AEA)
- Egyptian Veterinary Association of Epidemiology
- Association Mexicana de Epidemiology (AMEPID)
- Epidemiological Association of Bangladesh (EPAB)
- American Society for Public Administration (ASPA)
- French International Agency for Research on Cancer
- Cambodian Society of Infectious and Tropical Diseases
- International Society for Pharmacoepidemiology (ISPE)
- Tanzania National Institute for Medical Research (NIMR)
- Canadian Society for Epidemiology and Biostatistics (CSEB)
- Society for Pediatric and Perinatal Epidemiologic Research
- Southern African Clinical Epidemiology Association (SACEA)
- International Society for Environmental Epidemiology (ISEE)
- Indian Association of Preventive and Social Medicine (IAPSM)
- Association of University Programs in Health Administration, USA
- Association for Health and Environmental Development (AHED), Egypt
- Tunisian Environmental Exposure and Epidemiology Association (TEEEA)
- Cameroon Directorate for Combating Disease, Epidemics and Pandemics
- Association for Middle Eastern Public Policy and Administration (AMEPPA), USA
- Italian Society of Medical Statistics and Clinical Epidemiology / Societal Italian di Statistical Medical de Epidemiologic Clinical (SISMEC)
Public Health Institutes:
- Ghana Health Service
- Public Health England
- Public Health Wales
- Malawi Ministry of Health
- Jordan Ministry of Health
- Sudan Public Health Institute
- Public Health Institute of Chile
- Germany Robert Koch Institute
- Spain Carlos III Health Institute
- Saudi Arabia Ministry of Health
- Serbia Institute of Public Health
- China Centre for Disease Control
- Israel Center for Disease Control
- Italy National Institute of Health
- Albania Institute of Public Health
- Kenya Medical Research Institute
- Iceland the Directorate of Health
- Togo National Institute of Hygiene
- Pakistan Institute of Public Health
- Angola National Institute of Health
- Pasteur Institute of Morocco (IPM)
- CARICOM Ministry of Health (MoH)
- Guatemala National Science Center
- Turkey Refik Saydam Hygiene Center
- Norwegian Institute of Public Health
- Colombia National Institute of Health
- The Nigeria Centre for Disease Control
- Morocco National Institute of Hygiene
- Peru National Institute of Health (INS)
- Cambodia National Institute of Health
- Japan National Institute of Public Health
- Syria Center for Strategic Health Studies
- Portugal National Health Institute (INSA)
- Mozambique National Institute of Health
- Brazil FIOCRUZ (Oswaldo Cruz Foundation)
- Somalia National Institute of Health
- Thailand National Institute of Health
- Myanmar National Health Laboratory
- Ethiopian Public Health Institute (EPHI)
- Slovenia National Public Health Institute
- India National Centre for Disease Control
- Libya National Centre for Disease Control
- Moldova National Center of Public Health
- Croatia National Institute of Public Health
- Poland National Institute of Public Health
- Burundi National Institute of Public Health
- Hungary National Center for Epidemiology
- Ireland Institute of Public Health in Ireland
- Belgium Scientific Institute of Public Health
- Bangladesh National Influenza Centre (NIC)
- Denmark National Institute of Public Health
- Sweden The Public Health Agency of Sweden
- Palestinian National Institute of Public Health
Upcoming Conferences
- 12th International Conference on Pharmacoepidemiology and Clinical Research March 18-19, 2019 Dubai, UAE.
- 14th International Conference on Infectious Diseases, Prevention and Control March 21-22, 2019 Dubai, UAE.
- 25th International Conference on Human Metabolic Health- Diabetes, Obesity & Metabolism March 21-22, 2019 Dubai, UAE.
- 27th International Diabetes and Healthcare Conference July 18-19, 2019 Abu Dhabi, UAE.
- 14th World Congress on Healthcare and Medical Tourism July 18-19, 2019 Abu Dhabi, UAE.
- 8th World Congress on Public Health, Epidemiology & Nutrition July 10-11, 2019 Osaka, Japan.
- 2nd European Conference on Epidemiology & Public Health July 04-05, 2019 Paris, France.
- 11th International Conference on Epidemiology & Public Health September 26-27, 2019 Copenhagen, Denmark.
- 8th World Congress on Healthcare and Healthcare Management October 21-22, 2019 Tokyo, Japan.
- 5th World Congress on Public Health, Epidemiology & Nutrition November 25-26, 2019 Auckland, New Zealand.
- 4nd World Congress & Expo on Public Health, Epidemiology and Nutrition September 19-20, 2019 at MIAMI, USA.
- 3rd World Congress on Public health and Health care Management April 19-20, 2019 at Dubai, UAE
- 12th European Public Health Conference 20 - 23 November 2019 Marseille Chanot, Palais des Congrès et des Expositions, Marseille, France
- The 2nd Global Public Health Conference 2019 (GlobeHEAL) 14 th – 15 th February 2019 in Colombo, Sri Lanka
- 10th RSEP International Multidisciplinary Conference, January 15th-17th 2019, Bangkok, Thailand
- The European Precision Medicine Conference scheduled on September 23-25, 2019 in London, UK.
- Wessex Public Health Conference 2019 March 15th 2019 Britannia Road, Southampton
- Psychology, Neurology and Mental Health summit September 09-10, 2019 at London, United Kingdom
- International Health Congress, Oxford 2019 26th - 28th June 2019 St Margaret's Road, Oxford.
- The IRES - 559th International Conferences on Medical and Health Science (ICMHS) 9th - 10th February, 2019 in Athens , Greece
5 things you need to remember before buying health insurance policy
-
The most imperative thing to reflect on is the sum insured. If your medical expenses are above the total insured limit then it will not be allocated. It is sensible to check how much coverage you would require. It gets slightly difficult to raise the amount of sum guaranteed when you age.
- People at times are cannot decide whether if they should buy an individual policy or a family floater policy. Individual policies include a single person while the family floater covers the full family under one single policy. It is to be celebrated that for a young family, a family floater plan is much lesser than the individual plan. Another thing is that in an individual policy each member has a dedicated sum insured whereas in case of a family floater plan the insurance cover is mutual.
- While choosing among numerous health insurance plans, instead of lesser premiums considers the benefits which are been accessible. There are certain benefits like pre and post hospitalization, day-care measures, OPD, maternity extensions or emergency vehicle service, etc., should be taken into consideration.
- Often individuals have diseases before they apply for health policy. So, when applying for the policy, the insurance company insist on health check tests. On the basis of the report received, the company chooses if the policy application is to be accepted or rejected. If they choose to accept then they recommend a holding up period which is typically 4 years. It means that in case of any hospitalization fee related to the ailments confirmed can be claimed just after the completion of 4 successful years with the health insurance providers.
- Every health insurance company has tie-ups with clinics and hospitals across the nation which is known as empanelled hospitals. If you are conceded in empanelled hospital then you don't have to pay. All you need to do is to give your policy number and after that hospital and your insurer will take care of the remaining thing. So, much like a cashless treatment. As no claim reimbursement or documentation is required. If you get treated at a hospital which is not on the list of empanelled hospitals then you will not get cashless mediclaim.
The violence taking part in Congo debilitates combat against Ebola: Epidemiology Conference 2019
Subsequent to assaults on two Ebola treatment centers in the Democratic Republic of Congo recently, Doctors Without Borders says public health workers are “failing” to oppress the outbreak.
Medecins Sans Frontières (Doctors without Borders) were asked to stop their work at two treatment centers, which is in the centre region of current Ebola outbreaks in Democratic Republic of Congo after they were dreadfully damaged by two separate attacks. As a result of such violent behavior, the Ebola response is failing to put on the upper hand on the epidemic.
The epidemic, which began late in the month of August, has killed at least 569 natives, according to the World Health Organization.
Research says about the high health burdens of very high risk drinking: Epidemiology Conference
Alcohol is a psychoactive substance, causing a dependence-producing property that has been widely used in many cultures for centuries. The unsafe use of alcohol causes various disease, societal and financial burden in societies. Alcohol use is a causal factor in more than 200 ailment and injury conditions. Consumption of alcohol is linked with a risk of developing health issues such as psychological and behavioural disorders, as well as alcohol addiction, major non-communicable diseases such as liver cirrhosis, some cancers and cardiovascular infections, along with injuries follow-on from violence and road clashes and collisions. A significant proportion of the disease burden inferable to liquor consumption arises from accidental and deliberate injuries, together with those due to road traffic crashes, violent behaviour, and suicides and lethal alcohol-related injuries tend to occur in rather younger age groups.
In recent study conducted on the subject Addiction Biology, it was reported that the existence of Very High Risk Drinking Level (VHRDL), defined as drinking > 100g of ethanol/day, was found to be 0.74-0.85% in 13 European Union countries, including the risk of disease or injury of about 13.5 per 100 individual with VHRDL annually. Another such study based on the analysis carried out in 9 European countries showed that VHRDL leads to 43.8% of all pancreatitis, 41.1% among oral cavity and pharyngeal cancers and 53.6% in liver cirrhosis. Application of these figures to French Mortality data showed that the life expectancy of people with VHRDL is reduced 2-3 decades around 47-61 year only when compared with the general population.
This indicates the health burden of VHRDL is very high and measures need to be implemented to reduce the VHRDL while amending the public health policies.
Public health might have disregarded people with very high drinking levels and seen them basically like a small marginal who ought to be helped clinically in the health care organization. In spite of this, an additional systematic analysis shows that evident burden of disease is linked with this drinking pattern in and hence comprehensive approaches must be well thought-out.
To increase the production of Antimalarial compound in Plants, genetic engineering techniques are implemented : Epidemiology and Public Health Conference
Sweet wormwood, Artemisia annua, is the solitary resource of a powerful antimalarial compound called artemisinin. This antimalarial compound is recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO) as a cure for malaria caused by Plasmodium falciparum, but the source is presently is well below demand. Nearly half of the world’s population is at risk of malaria.
Researchers used the genome sequence of Artemisia annua to boost the plant’s capacity to make artemisinin. They used the genome sequence of A. annua, and genetically tailored the plant to deliver much higher levels of artemisinin. This might be a good strategy for the large-scale generation of artemisinin which can meet the ever-increasing need for this medicinal compound and help deal with the global health problems.
A. annua produces artemisinin on a rate of only roughly 0.1 percent to 1 percent of the dry weight of its leaves. Other approaches to produce this compound has mainly centred on making the drug through other means, for example, via yeast cells designed to produce a biochemical precursor to artemisinin. But that approach is costly and is not yet ready to substitute plant-based generation.
In the recent study, Research scientist have put together a high-quality design assembly of the A. annua genome and used it to classify the genetic components of artemisinin biosynthesis. By raising the expression of three genes implicated in this pathway, the team was able to grow plants with much higher levels of artemisinin—up to 3.2 percent of the leaves’ dry weight.
This accomplishment, building as it does on earlier molecular breeding and genetic designing attempts. Before the work could have an influence on commercial assembly it will necessitate extensive field trials to reveal that the engineered plants function in the field is the same as they have done under investigational conditions.
An Aging Immune System may describe Age-related Cancer Risk : Epidemiology Conference
The key to cancer avoidance possibly lies in the immune system rather than inherent mutations, the recent focus of most anti-cancer efforts around the globe, according to a most important novel investigate done.
For decades, it has been acknowledged that transformations emerging either as an end result of genetic predisposition or standard of living and ecological factors cause cancer. The conventional view is with the aim of the way cancer occurrence increases with age may possibly be understood and evaluated if multiple (typically five to six) mutations in a single cell are necessary to set off cancer.
The failing immune system with we age may possibly be a stronger case for the rising incidence of early cancer than multiple mutations.
Following the theory that an aging immune system may outcome in higher rates of cancer, just as it leads to older person is more inclined to other diseases; they looked at statistics on 2 million cases of cancer with the age ranging between 18-70. A mathematical equation is developed for how they would anticipate cancer prevalence to increase in relative to a failing immune system and compared it to the age profiles for 100 distinct cancers.
Their model fitted the statistics better than the several mutation hypotheses. As the immune system normally declines more slowly in women than men, they were also capable to report for the sexual characteristics difference in cancer occurrence, something that transformations alone cannot explain.
This proposes that the immune system, especially as it gradually fails, may perform a greater role in the advancement of cancer than earlier thought. If borne out by additional studies, this might have significant implications for cancer prevention and treatment around the world.
Almost all of the typical research into cancer is based on how we can comprehend genetic mutations, aim them and thereby treat the disease. whether mutations unaided can be related for the swift rise in cancer prevalence with age while aging causes other significant changes in the body.
The main cause of immune aging is the withdrawal of the thymus organ. It is the place where T cells, circulate the body killing dysfunctional cells or foreign agents, are produced.
Thymic involution starts from approximately the age of one and the thymus generally halves in size every 16 years, with a resultant fall in the production of T cells. The analysts found a very strong connection between the chances of certain cancers expanding and the new T cell populaces deteriorating.
Epidemiology of Sexual Transmission of Zika virus (ZIKV) described by the Living Systematic Study : Public Health Conference
Zika virus (ZIKV) can be sexually transmissible within a shorter period of time than earlier evaluated, concurring to a systematic study carried out. The study included an analysis of data from both human and animal studies and was conducted to explain the epidemiology of sexual transmission of ZIKV.
Sexual transmission of ZIKV has been earlier documented, but the dangers of transmission are not well implicit, and it is not identified whether other flaviviruses can be transmitted by this means. To address this gap in information, the analysts conducted a methodical review of available, relevant evidence. Sexual transmission of ZIKV is found to be more prominent to spread from men to women than from women to men. For sexual transmission of ZIKV, it was found by researchers that the average serial interval, the time between the start of indications in 2 sexual partners is 12 days, and the average duration of ZIKV RNA determination in semen is longer (34 days) than in the female genital tract (12 days). There was no evidence for sexual transmission for any other arthropod-borne flaviviruses.
The study's conclusions are constrained by the underlying indication, which might have outstanding biases. On the other hand, the study is developed as a living methodical examination, such that more up to date evidence will be included upon accessibility. Of public health pertinence, this study suggests that the communicable period for sexual transmission of ZIKV is shorter than estimates from the initial post-outbreak considers.
Dealing with the Salmonella Epidemic, a Sneaky Superbug : Healthcare Conference
In today’s world the ever increasing reliability on antibiotics and other disease preventive drugs have sprung several mutated strains of multi-drug resistant microbes AKA superbugs. Salmonella is one such strain and are known to cause frequent epidemic outbreaks. They grow well on raw meat products such as chicken, fish, beef, ham, etc. Since, humans consume these products almost on a daily basis and it isn’t difficult to get infected and outbreaks are more common than you think.
The most common symptoms observed in a salmonella infection are, diarrhea, fever and stomach aches which show up 12 to 72 hours after the initial exposure. It is relatively, a treatable illness but the strains mutate and transform into more resilient forms and new more potent drugs are necessary to combat them. With the proper treatment the infected person could be cured within 4 to 7 days. Inflammation of the intestines is one of the obvious characteristics of salmonella infection and due to the tissue damage caused the pathogen can migrate into other parts of the body through the blood stream. Children under 5 and older adults above 65 can suffer severe illness due to their weakened or underdeveloped immune systems. In rare cases, deaths have also been reported. So, yes it is a grave matter of concern, given the frequency of outbreaks.
The Centre of Disease Control (CDC) and other health officials have identified salmonella infected raw chicken meat as one of the major contributors for the recent outbreaks in the U.S and are making attempts to contain the spread of the infection.
The CDC is also handing out a few important but basic methods to significantly reduce the infection and its spread. These advisories are linked to cooking and food preparation methods. Performing these tasks can significantly reduce the chances of picking up the infectious microbe.
- Hand Wash: Salmonella is transferable from an infected individual to others by interactions with the hands. Therefore, washing hands before and after eating or cooking meat or after contact with animals or changing diapers.
- Thorough cooking of chicken meat: With careful food preparation methods it is possible to eliminate salmonella in large proportions. Cooking with an internal temperature of 165°F and also reheating the leftovers with the same temperature is enough to kill most of the microbes. Internal temperature can be measured using a food thermometer to ensure even the thick sections of the meat receives the heat treatment.
- Avoid spreading microbes from chicken meat in food preparation areas: Reduce the area of contact of the raw meat. Washing the meat prior to cooking is not recommended. After, food preparation, clean all the surfaces of contact, utensils, cutting boards with warm water followed by soapy water.
Anti-biotics may be one of the most important and useful inventions to come out in the history of medicine and have saved countless lives since time period of world war 2, but nature always has tricks up her sleeves. Microbes will constantly keep evolving and become more resistant to any kind of antibiotics we throw at them. So, we definitely need an alternative or we will be facing an impossible to kill superbug.
Epidemiology of Malarial Contamination : Public Health Congress
Epidemiologists have recently paid more prominent consideration in the past to the study of disease transmission of clinical malaria as opposed to the epidemiology of malarial contamination. This alters of emphasis has been stimulated in portion by the requirement for superior clinical definitions of malaria within the assessment of control measures such as insecticide-treated materials and malaria immunizations. Nearly half of the entire world populace is exposed to the chance of contracting malaria. Malaria could be a life-threatening malady caused by parasites that are transmitted to individuals through the bites of contaminated female Anopheles mosquitoes. It is preventable and curable. Malaria is caused by Plasmodium parasites. The parasites are spread to individuals through the bites of infected female Anopheles mosquitoes, called "malaria vectors." There are 5 Plasmodium parasites species that cause malaria in people: Plasmodium falciparum, P. vivax, P. malariae, P. ovale and P. knowlesi and 2 of these species – P. falciparum and P. vivax – pose the greatest risk. Malaria influences basically poor tropical and subtropical regions of the world. Where the infection is endemic it is the driving cause of ailment and passing.
Usually, malaria is transmitted through bites of female Anopheles mosquitoes. There are more than 400 diverse species of Anopheles mosquito; around 30 are malaria vectors of major significance. The intensity of transmission depends on components related to the parasite, the vector, the human have, and the environment. Anopheles mosquitoes lay their eggs in water, which bring forth into hatchlings, in the long run rising as grown-up mosquitoes. The female mosquitoes look for a blood supper to sustain their eggs. Each species of Anopheles mosquito has its possess favored aquatic territory; for example, a few prefer little, shallow collections of new water, such as puddles and foot prints, which are abundant during the rainy season in tropical nations.
Early diagnosis and treatment of malaria diminishes malady and avoids passings. It too contributes to decreasing intestinal sickness transmission. The finest accessible treatment, especially for P. falciparum intestinal sickness, is artemisinin-based combination treatment (ACT). RTS, S/AS01 (RTS,S) – too known as Mosquirix – is an injectable vaccine that gives partial security against jungle fever in youthful children. The vaccine is being assessed in sub-Saharan Africa as a complementary malaria control tool that possibly can be included too (and not replace) the core package of WHO-recommended preventive, diagnostic and treatment measures.
Malaria is still considered a worldwide health issue and a major killer. Morbidity and mortality burden of malaria can be decreased strengthening prevention, moving forward malaria diagnosis, using correct treatments based on artemisinin combination and adopting procedures pointed at preventing drug resistance. Real malaria frequency is difficult to get. However, it is possible to create reliable estimates much appreciated to the information provided by Ministries of Health of different countries and to exact predominance studies. Determination of real rate of malaria and assurance of the real Plasmodium species distribution are two diverse issues that could offer assistance expert in the eradication of malaria, the real and unique objective within the battle against malaria.
All Infectious Diseases Show Seasonal Outbreaks : Epidemiology Conference
The majority of us are aware of the seasonal phase of influenza outbreaks, which intended to peak in the winter for Americans. One of the PhD, a scientist at the Columbia Mailman School of Public Health, makes a case that all communicable diseases are inflicted with a seasonal factor.
Data from the World Health Organization, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and peer-reviewed publications to create a calendar of epidemics for 69 infectious diseases, from commonplace diseases to rare tropical diseases. A specified year outbreaks of flu in the winter, chickenpox in the spring, and gonorrhea and polio in the summer--to name a few of the best depicted regular seasonal outbreaks.
It was found seasonality occurs not just in acute infectious diseases like flu but also chronic communicable diseases like Hepatitis B, which depending on geology, flares up with greater normality certain period of the year. Introductory work has revealed that even HIV-AIDS has a seasonal factor, thought to be driven by seasonal changes in the lack of healthy sustenance in agricultural settings.
The four main drivers of seasonality in infectious diseases. Ecological factors like heat and moisture control seasonal flu; in vector-borne infections like Zika too, the surroundings play a role in the propagation of mosquitos. Host behaviors such as children coming into close vicinity with each other during the school year are the aspect in measles. Environmental factors such as algae play a role in the outburst of cholera. Seasonal biological rhythms, alike to those that dominate relocation and hibernation in animals, may also be a cause in diseases like polio, though more research is needed.
Seasonality is an influential and general feature of infectious diseases, in spite of the fact that the scientific community has largely overlooked it for the majority of infections, Much effort is needed to comprehend the forces driving infection seasonality and know how we can control seasonality to model intercessions to anticipate flare-ups and cure chronic infections.
Recognizing the drivers of seasonal flare-ups is not always clear, but can pay dividends. For example, the microorganisms that cause cholera, which spread to humans by fecal-oral transmission, can be maintained in water upheld by algae. Public health authorities might take on an intervention to inhibit the transmission of cholera from infected individuals and/or target the microorganisms present in algae-filled waterbodies; significantly, the key season to embark on each of these intercessions would probably disagree.
In the case of polio, public health analysts previously thought summer flare-ups were driven by the seasonal blending of children in swimming pools or theaters or by the climate, but not one or the other of these factors could explain the late spring outbreaks around the globe. In 2001, an associate at the CDC hypothesized that seasonal changes in the hormone melatonin may well play a role in tweaking the immune system. In one of the ongoing study investigated this possibility by comparing levels of immune molecules in blood drawn from patients at different intervals of the year.
Research reveals about the Unseen Infections harming world's Children and Adolescent Health : Epidemiology Meet 2019
Children all over the globe are distress from unobserved infections that are hindering their progression and mental development, novel research from an international coalition of researchers uncovers.
Up to 30 percent of children in low-resource nations experience underdeveloped growth. Insufficient nutrition and diarrhea have long been held responsible, but researchers have, until now, been incapable to justify a large percentage of stunting cases. Two new considers, however, demonstrate that a huge number of children with no signs of diarrhea are carrying dangerous infections. These diseases eventually inhibit them from getting their full potential and propagate a cruel phase of lack.
The only focus on diarrhea, may not be adequate. We need to be addressing these asymptomatic exposures too. If we could have intercessions beside just four pathogens, we would anticipate development in the progression that's alike to what has been seen for nutritional interventions in comparative settings. This puts pathogen exposure, in terms of significance, on the equivalent level as nutrition, which in the past has been well thought-out the main cause for deprived growth.
Conference Highlights
- Epidemiology and Public Health
- Health and Nutrition
- Oral & Dental Health
- Cancer Epidemiology
- Veterinary Public Health
- Nursing and Health care
- Child and Adolescent Health
- Health Systems and Economics
- Chronic and Infectious Diseases
- Healthcare & Hospital Management
- Mental Health and Mental Disorders
- Cardiac Disorders & Its Complications
- Metabolism and Metabolic Disorders
- Public Health Policy and Administration
- Environment, Climate and Urban health
- Biomedical and Health Care Technologies
- Reproductive Medicine & Women’s Health
- Case Report on Epidemiology and Public Health Research
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | June 17-18, 2019 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | Day 1 | Day 2 | |
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
- Epidemiology: Open Access
- Journal of Community Medicine & Health Education
- Journal of Tropical Diseases & Public Health
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by







































